Relativitaet auf dem Pruefstand
Doppler Effect
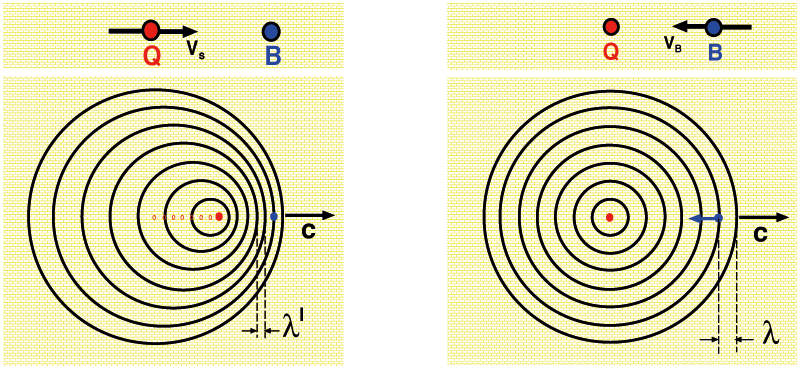
The effect named after the austrian physicist Christian Doppler relates to the propagation of waves in the case that the source of the wave and the observer move relative to each other.If the source and the observer move towards each other, the observer experiences a higher frequency compared to the frequency at the source. If they separate in time the observer measures a lower frequency. This effect can easily be experienced for sound waves. In the case of relativity theory the Doppler effect relates to light waves.
[ Sitemap ]
[ info ] This website was created by the MPI for the History of Science.
 Scene
Scene


 1st Slide
1st Slide
 Branching Point
Branching Point
 Module: Relativitaet auf dem Pruefstand
Module: Relativitaet auf dem Pruefstand Sequence: Start
Sequence: Start Slide:
Slide:  Branching Point: Putting relativity to the test - Was Einstein right ?
Branching Point: Putting relativity to the test - Was Einstein right ? Back
Back

