Astrophysik: Gravitationswellen
Neutron stars and gravitational waves
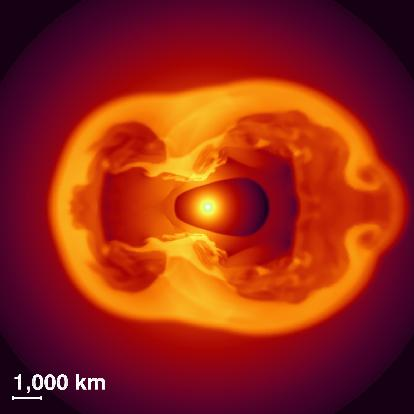

When massive stars run out of nuclear fuel, they explode in a gigantic supernova. What remains is a neutron star - an extremely compact heavenly body. This compactness makes neutron stars into potentially very effective sources for gravitational waves. This is true already for their creation: The image on he left shows a computer simulation of the collapsing core region of a supernova; the brightness of a region denotes its density. The extremely dense matter undergoing acceleration in an asymmetric explosion and collapse leads to the emission of gravitational waves.
[ Sitemap ]
[ info ] This website was created by the MPI for the History of Science.
 Scene
Scene


 1st Slide
1st Slide
 Branching Point
Branching Point
 Module: Astrophysik: Gravitationswellen
Module: Astrophysik: Gravitationswellen Sequence: Gravitationswellen Einstieg
Sequence: Gravitationswellen Einstieg Slide: Gravitational Waves
Slide: Gravitational Waves Branching Point: Gravitational waves
Branching Point: Gravitational waves
