The most promising current detectors work in a different way. They are called interferometric gravitational wave detectors, and they use laser light to monitor precisely the distance between freely suspended test masses. A gravitational wave passing through such a detector would change these distances in a characteristic way. More information about these detectors can be found in an extra sequence How does an interferometric gravitational wave detector work? on this media station.
The image shows a view of the British-German detector GEO 600. The laser light travels from the hut in the foreground to mirrors suspended at the end of 600 metre long arms, visible in the image on top and to the right.
 Scene
Scene


 1st Slide
1st Slide
 Branching Point
Branching Point
 Module: Astrophysik: Gravitationsdetektoren
Module: Astrophysik: Gravitationsdetektoren Sequence: Gravitationswellendetektoren Einstieg
Sequence: Gravitationswellendetektoren Einstieg Branching Point: Gravitational wave detectors
Branching Point: Gravitational wave detectors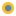 Slide: Detecting gravitational waves
Slide: Detecting gravitational waves Back
Back


